Iron and Phosphorus Reduction Production of
Process for Rotary Kiln Process, Operation Requirements and Recommended Parameters
I. Rotary Kiln Direct Reduction Process Process
1. Rotary Kiln Process
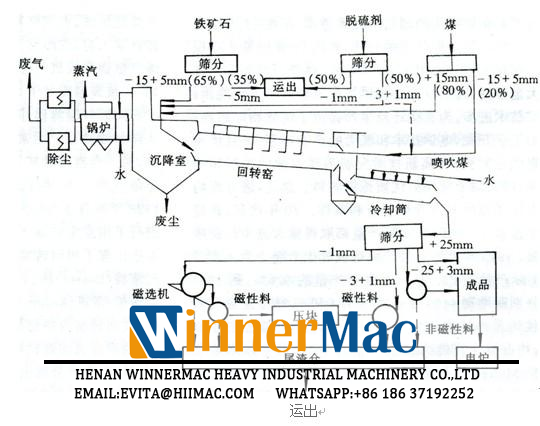
Generally shown in the above figure (the process flow used by Jiuyi Mining is not exactly the same as the above figure). The rotary kiln is a cylindrical high-temperature reactor in which the refractory material can be continuously rotated while being placed at a slight inclination on a plurality of sets of support rollers. During operation, a certain particle size of raw materials (iron oxide scale), partially reduced coal (including return carbon) and desulfurizer are continuously added from the kiln feed end (tail end) in proportion, as the kiln body rotates (0.5 to 1.2 r/min). The material is brought up to a certain height by friction and rolls down due to gravity, while moving forward to the kiln discharge end (low end) by a small distance. At the discharge end of the kiln, there is also a reduced coal spray to the, and the reduced coal of suitable granularity is sent into the kiln by high pressure air, and the sprayed air amount can be adjusted to effectively control the injection distance and distribution. The heating and reaction heat of the material in the kiln is fed into the air (primary wind and secondary air) by the discharge end and the supply duct extending into the kiln along the length of the kiln, and the volatile matter and reduction reaction released by the reduced coal in the combustion kiln The generated CO and carbon are provided. If the heat is insufficient, a pulverized coal burner can be added to the kiln head to supplement it. The material is gradually heated by the reverse hot gas flow during the advancement process to complete drying, preheating, carbonate decomposition, desulfurization, iron oxide (or other elemental) reduction and carburization reaction. Adjusting the air supply volume of each duct, the quantity, size and distribution of coal powder and reduced coal, can flexibly control the temperature and distribution in the kiln. The iron ore entering the kiln is allowed to stay in the kiln for 8 to 10 hours and at 950 to 1100 °C to transform into sponge iron.
The high temperature material discharged from the discharge end falls into the cooling cylinder through the chute. Spray water outside the cylinder (or both inside and outside) to cool the material below 120 °C. In order to improve the material movement and strengthen the cooling, the cylinder is equipped with a lifting plate. Sealing devices are installed at the discharge end of the rotary kiln and at both ends of the cooling cylinder to maintain a slight positive pressure during production to prevent re-oxidation by air inhalation. The cooled material is subjected to sieving classification and magnetic separation to obtain magnetic pellets (direct reduced iron), magnetic powder, non-magnetic pellets and non-magnetic powder. The non-magnetic pellets contain higher fixed carbon and can be reused as a reducing agent.
2. Rotary kiln equipment The
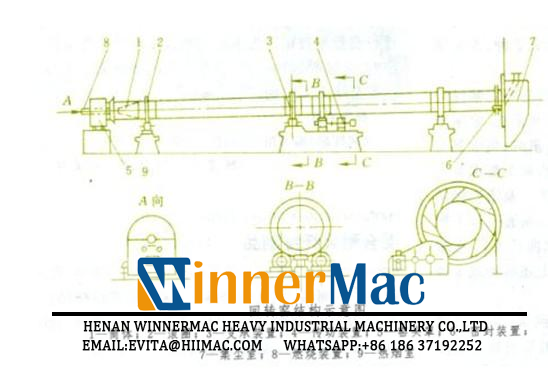
rotary kiln equipment is mainly composed of cylinder, rolling ring, supporting device, transmission device, kiln head cover, sealing device, dust collecting chamber, combustion device and hot smoke chamber. See the above figure for details.
(1) Cylinder. The cylinder of the rotary kiln is rolled from a steel plate, and has been developed from riveting to all welding. The barrel should have sufficient stiffness and strength to ensure linearity of the axis and roundness of the section during installation and operation. The cylinder is lined with refractory material to protect the simplified body and reduce heat dissipation. The simplified lining brick should meet the requirements of operating conditions. The pre-tropical zone generally adopts clay bricks, and the firing zone is selected according to factors such as calcination temperature and chemical corrosion. The rotary kiln for calcining iron ore is usually made of clay brick or 3 equal height aluminum brick. The kiln mouth guard plate is arranged at both ends of the cylinder body to prevent the cylinder body from being deformed and cracked due to the action of hot material or high temperature smoke, and the kiln lining of the cylinder body is detached. Since the working temperature of the kiln mouth is sometimes as high as 1000 to 1300 °C, the kiln mouth shield should be made of heat-resistant and wear-resistant materials that can be replaced, and if necessary, air-cooling or water-cooling measures.
(2) Rolling ring. Simplifiedly equipped with a number of rolling rings (belts), the cylinder is divided into several spans. The weight of all the swivel parts, such as the simplified body, the kiln lining, the material and the kiln skin, is transmitted to the support device through the rolling ring. The rolling ring is cast or forged by carbon steel and alloy steel with good wear resistance and high contact fatigue strength. There are two types of rolling ring cross-sections: rectangular and box-shaped. Most of them currently use rectangular cross-section rolling rings. A moderate gap is left between the rolling ring and the cylinder to enhance the rigidity of the cylinder without causing large thermal stresses on the cylinder and the race.
(3) Supporting device. Withstand the full weight of the rotating equipment. It has an axial and radial positioning function for the simplified and safe operation. The supporting device is composed of a supporting wheel, a carrier shaft, a carrier bearing, a retaining wheel and a base. The roller directly contacts the raceway. The axis of each set of rollers must be parallel to the centerline of the simplified body, and the three-point line between the center of the two sets of rollers and the center of the section of the cylinder should form an equilateral triangle. The width of the roller is slightly wider than that of the rolling ring. It is made of wear-resistant cast steel. The cross section of the roller has three kinds of structures: single-rotary, double-rotor and three-wheel. The installation method includes two types: spindle type and shaft type. The shaft type pulley shaft is generally a heat fit assembly. The structure of the roller bearing is divided into a sliding bearing, a rolling bearing and a sliding bearing, and most of them adopt a sliding bearing. The lining of the sliding bearing is set on the spherical tile to form a spherical contact, which can automatically adjust the heart. The oil spoon is lubricated with oil, the spherical corrugated water is cooled, the shaft end is provided with a thrust plate, and the shoulder has a thrust ring to bear the axial direction. thrust. The bearing is fixed to the steel base and has a top wire for adjusting the position of the roller. Although the rolling bearing has the advantages of simple structure, low frictional resistance and low power consumption, the large-capacity one-time investment is large, and the service life is lower than that of the sliding bearing. In addition to the former Soviet Union using rolling bearings on the support of large-diameter rotary kiln, rotary kiln in the United States, Denmark and Japan use sliding bearings. China only uses rolling bearings on small and medium-sized rotary kiln. The role of the retaining wheel is to limit or control the axial movement of the cylinder. The number of sets of kiln support devices is called the number of kiln gears. The gear wheel can be mounted on the first or several-speed support device, which is called the gear wheel support device. In addition to the hydraulic gear wheel, a set of gear wheels are generally installed only on both sides of the race ring near the large ring gear. The wheel is divided into "signal wheel", "thrust wheel" and "hydraulic wheel" according to its function. Most of the "signal stop" is used in old kiln. It is not a stop device to prevent axial turbulence of the kiln. It only acts as a signal. The “thrust retaining wheel” receives the sliding force of the kiln and limits the axial movement of the cylinder. The “hydraulic retaining wheel” pushes the retaining wheel through the hydraulic device, forcing the simplified axial movement to ensure uniform wear of the rolling ring and the supporting roller over the full width and simplified linearity to reduce power consumption. This kind of device can simultaneously adopt several small hydraulic retaining wheels to jointly withstand the axial yoke power of the kiln, and is especially suitable for rotary kiln with large diameter and multiple gears.
(4) Transmission. The power is transmitted to the large ring gear fixed to the simplified body by the deceleration mechanism, so that the cylinder rotates slowly. Due to transportation and installation requirements, the ring gear is split in two halves and its number of teeth is even. The spring plates are available in both tangential and longitudinal directions. The kiln transmission device is characterized by large transmission ratio, smooth and stepless speed regulation, and large starting torque. It is divided into two systems: main drive and auxiliary drive. The main drive system is mostly composed of a main motor, a main reducer, a gear and a large ring gear. It can also be connected with a semi-open gear or belt drive in the middle, or a double drive with two sets of motor and speed reduction mechanism. The main motor should have a speed control function.
The function of the auxiliary transmission system is to periodically rotate the kiln body when the main motor or main power supply fails, to avoid deformation and bending of the cylinder body, and also used in kiln brick laying or maintenance. The auxiliary reducer is driven by the auxiliary motor and connected to the high speed shaft of the main reducer through the clutch. The auxiliary motor and the main motor are respectively powered by different power sources. The auxiliary motor can also be replaced by a diesel engine.
(5) Kiln hood. The cylinder head and the cooling device are connected to the kiln, and the clay brick is built in the hood, and a fire hole and an inspection door for monitoring the combustion of fuel and materials in the kiln are provided. The kiln head cover is available in both fixed and mobile versions. Large rotary kiln is mostly fixed.
(6) Sealing device. Prevents the inhalation of air from the gap between the rotating parts of the kiln and the fixture, or the gas carried by the kiln. There is a kiln head, a kiln tail seal, a seal between the kiln head cover and the simplified body is called a kiln head seal; the seal between the dust collection chamber and the simplified body is called a kiln tail seal. The basic requirements of the sealing device are firstly good sealing performance, and can adapt to the simplified roundness tolerance value and axial yaw amplitude during operation; in addition, the structure is simple, the maintenance is convenient, the wear resistance is not affected, and the thermal system of the kiln is not affected. There are three types of sealing devices: labyrinth (curved), contact (friction) and airtight. It is also possible to combine the above two or three types.
(7) Dust collection room. It is located at the end of the kiln and is made of red brick. The clay brick is built inside and the external steel frame is strengthened. The top is provided with a feeding pipe to feed the material directly into the kiln, and the flue gas enters the dust collecting chamber from the tail of the kiln. Due to the reduced flow rate, a part of the dust settles indoors, the side wall is provided with a flue gas exhaust pipe, and the lower part of the room is provided with a dust cleaning door or Mechanical ash device. When the preheating device is used at the kiln end, there is no dust collecting chamber.
(8) Combustion device. Depending on the fuel, the combustion unit has a coal injection pipe, a fuel burner and a gas burner. The combustion device is mounted on the bracket and extends from the kiln head into the kiln in the form of a cantilever. The support frame is provided with a burner adjustment mechanism for adjusting the position of the flame.
(9) Hot smoke room. It is located in the lower part of the kiln head cover, is made of red brick, is lined with clay bricks, and is reinforced with steel frame on the outside. The middle part of the middle part is provided with a lower material opening, and the material which is calcined in the rotary kiln is slid to the cooling device. After the cold air entering the cooling device is exchanged with the material calcined in the rotary kiln, the temperature can reach 500 °C, and is sucked into the kiln by the smoke exhausting device for use as secondary air. The side wall of the hot smoke chamber is equipped with a small door for observing and handling the crusted material.
Third, rotary kiln and thermal system operation requirements
1, rotary kiln model and production capacity
φ 2.5X38 m rotary kiln, one; direct reduction of annual production capacity of reduced iron is 62,000 tons, Taiwan production 20 ± 2 tons.
2, coaloperation
injectionkiln head coal injection total of 7.0 ± 0.5 tons / hour, fine coal gun pressure control at 60KPa, fine coal gun pressure control 10 ~ 14KPa. The kiln tail coal control is controlled at 800 ± 50Kg/h, and the excessive kiln tail coal quantity is strictly prohibited.
The North University of Science and Technology test shows that: at the reduction time of 70 minutes and the reduction temperature of 1050 °C, the reduced iron grade, metallization rate and compressive strength increase with the mass ratio of the reduced coal/iron ore. When the mass ratio is 2 The index is the best. When the mass ratio is 4, it starts to decline. Therefore, the suitable mass ratio is 2-4, preferably 1025-1040 °C.
3, kiln temperature control
kiln head box <980 °C, 1, 2, 3 galvanic control at 1000 ~ 1040 °C, short-term temperature should not exceed 1060 °C; 4, 5, 6 galvanic control at 1000 ± 20 °C; The galvanic couples 7, 7, and 9 are controlled at 950 ~ 1000 °C; the temperature of the cold smoke chamber is controlled below 700 °C. The temperature of the preheating section is controlled at 850 ~ 920 °C; the temperature of the transition section is controlled at 550 ~ 650 °C; the temperature of the drying section is controlled at 250 ~ 350 °C; the temperature of the bellows of No. 1 and No. 2 is not less than 600 °C.
The North University of Science and Technology test showed that: under the condition of reducing coal/iron=2 under the reduction time of 70 minutes, the reduced iron grade, metallization rate and compressive strength increased with the temperature (950-1075 °C), when 1025 °C, The reduced iron grade is the highest and the metallization rate is the highest. When the pressure is 1050 °C, the compressive strength is the largest, so the suitable reduction temperature is 1025-1050 °C, preferably 1025-1040 °C.
4, rotary kiln speed control
kiln body rotation speed is generally 0.5 ~ 1.2r / min. Rotary kiln motor speed is controlled at 400 ~ 440 rev / min, the main fan's regenerative air valve opening is 45% ~ 50%, the speed is 800 ~ 850 rev / min, the return air inlet negative pressure 780 ± 20KPa, temperature 310 ~ 350 °C . The drying fan valve opening degree is 65% to 70%, and the rotation speed is 800 to 850 rpm.
The North University of Science and Technology test showed that the reduced iron grade, metallization rate and compressive strength increased with the increase of reduction time at a mass ratio of 2 and a reduction temperature of 1050 °C. When the reduction time was 70 minutes, the index was the best.
5, the technical key to operation
(1) to ensure the reduction atmosphere in the kiln, control the air volume;
(2) control the appropriate temperature of the various parts of the kiln, do not allow the gangue to melt;
(3) the discharge end of the kiln maintains a slight positive pressure , 20 — 30 Pa.
Fourth, the rotary kiln ring control operation requirements
1, the cause of
the ring ring is mainly in the middle of the kiln, usually caused by the formation of low melting point silicate compounds at the high temperature of the sudden fluctuation of the kiln temperature. The large amount of powder in the kiln material or the powdering after entering the kiln is the material basis for the formation of the ring. Temperature fluctuation is the direct cause of the formation of the ring.
2, the principle of preventing ring
formation According to the original, fuel properties, a reasonable kiln temperature system and reduction process, to avoid high FeO materials, gangue and coal ash into the high temperature zone to produce low melting point compounds.
3. Measures to prevent ring formation
(1) In the 1980s, the high-reactive reduction coal was used to reduce the reduction operation temperature;reduction
(2) The kiln head injectioncoal technology was adopted to fully utilize the volatile matter in the coal to improve the coal activity and improve the kiln. Internal temperature distribution to prevent hot spots;
(3) Improve kiln temperature detection technology;
(4) Pay attention to raw material selection and strengthen raw material treatment, prevent powder from entering kiln, increase kiln filling rate, increase heat stability, and strengthen material layer protection;
(5) Increase the pressure in the kiln and strictly control the atmosphere.
The production practice shows that by adopting the above five measures, the occurrence of the ring failure is fundamentally eliminated, and stable production for 18 to 20 months is achieved.
June 2, 2018